Scientists have researched and made a list of creatures that may “share the same fate” with us in the next few thousand years. Surely you will not be surprised when you see their strange shape.
1. “Long-legged” bats
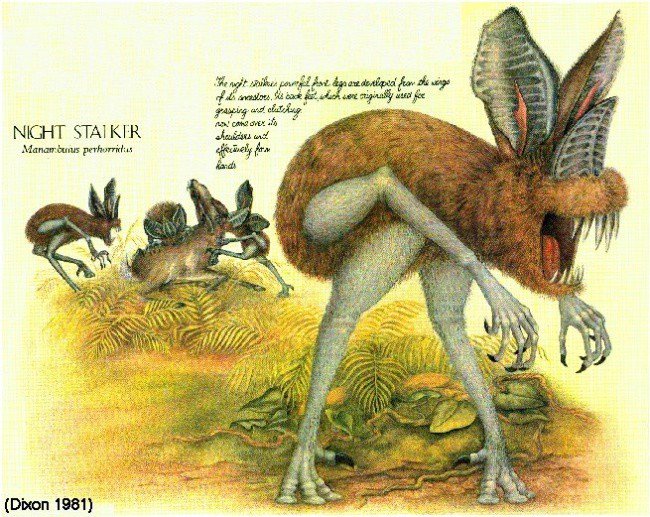
The bat species that is predicted to “descend” to Earth in the future has the scientific name Manambulus perhorridus. This species of bat has a rather strange shape with long, big legs, the wings seem to be less active than before and have a more strange positioning mechanism, the ears and nose may be paralyzed.
2. Necropteryx
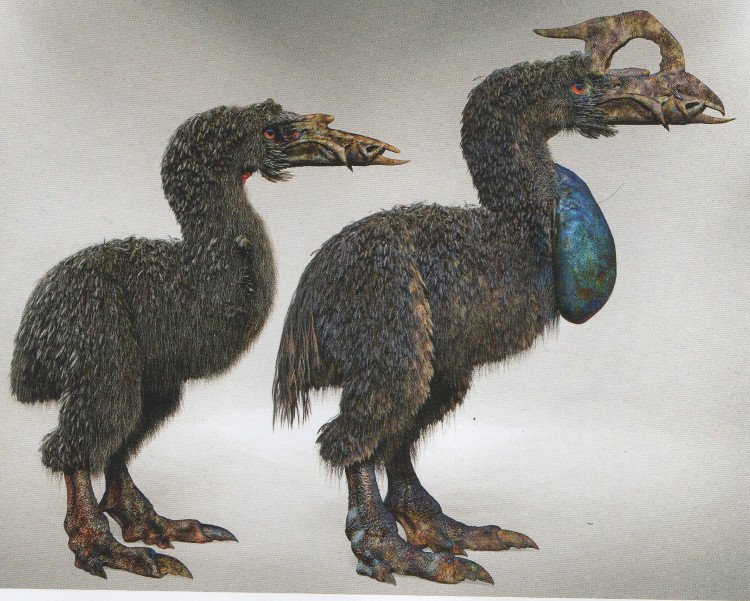

This strangely shaped creature is called Necropteryx, a combination of birds, kites and vultures. They have quite large beaks because they are responsible for biting and breaking bones while eating dead people’s bones.
Necropteryx did not have wings so they walked. To search for food, they can travel up to 10km per day. In particular, Necropteryx lays eggs on animal corpses and then they consider it their nest.
3. “Umbrella tail” mouse
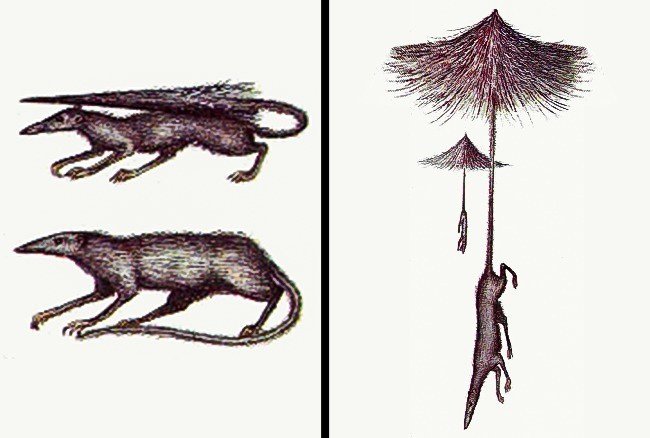
Through the evolutionary process, after several thousand years, the umbrella mouse species will appear on Earth, specifically North America. They were the first animals to use their tails for balance. This rat’s food is insects and they use their legs to jump and catch prey in the air.
4. Dancing demon Daemonops rotundus
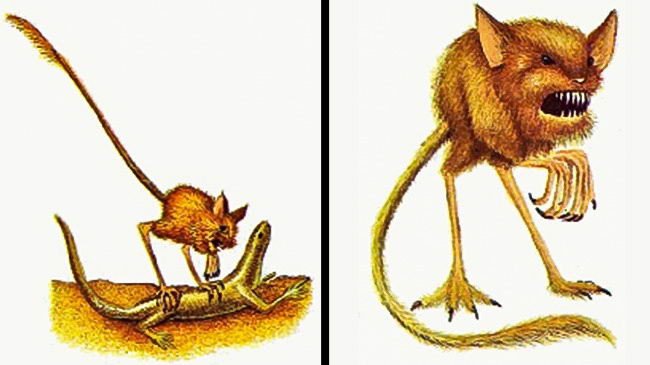
This monstrous-looking creature with the face and body of a mouse, long ears like a bat, and long, strong legs like that of a kangaroo is called the dancing devil Daemonops rotundus . With such physical characteristics, they are truly a desert predator. They use their long legs to hop like kangaroos, crossing long distances in the desert.
5. Termite Terabyte
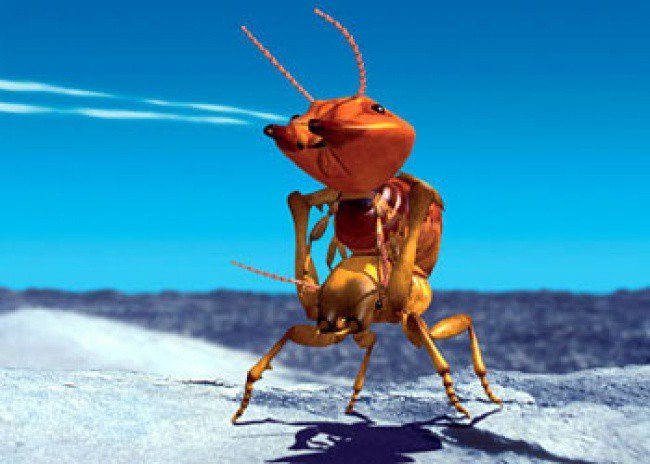

This new species of insect appearing in the future can defeat its prey with a weapon system that uses extremely powerful chemicals. Their food is algae.
6. Wakka
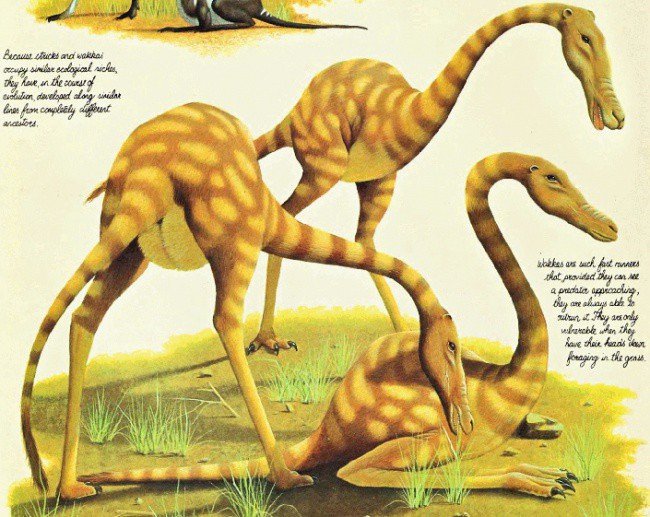
Anabracchium struthioforme, or wakka, is a giant creature with a rather strange structure, with no forelimbs, long hind limbs, and a neck nearly as long as its legs to help balance gravity. Their food is grass and they live mainly in South American grasslands.





